KINEMATICS
어떤 물체의 운동 상태는 다음과 같이 표현 할 수 있다.
public struct Kinematic
{
public Vector3 position;
public float orientation; // x-z 평면에서 +z축으로부터 시계방향 각도.
public Vector3 velocity;
public float rotation; //각속도
}
그러나 이거 가지고 운동을 표현하기는 조금 어색한데, 가속도의 개념이 빠져있기 때문이다. 따라서 외부에서의 힘(가속도)는 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있다.
public struct SteeringOutput
{
public Vector3 linear; // 가속도
public float angular; // 가속도(각)
}
이걸로 운동 상태를 업데이트한다면,
void Update(SteeringOutput steering, float deltaTime)
{
//위치 갱신
float half_t_sq = 0.5 * deltaTime * deltaTime;
position += velocity * time + steering.linear * half_t_sq;
orientation += rotation * time + steering.angular * half_t_sq;
//속도 갱신
velocity += steering.linear * time;
rotation += steering.angular * time;
}위와 같이 될 것이다.
그런데 deltaTime이 굉장히 작은 경우 [steering.linear * half_t_sq] 도 굉장히 작기 때문에 이걸 생략할 수 있다. (deltaTime을 0에 수렴시키면 적분이니까)
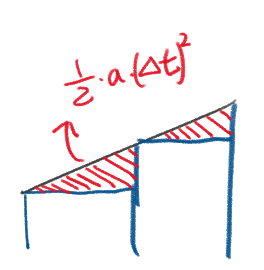
void Update(SteeringOutput steering, float deltaTime)
{
//위치 갱신
position += velocity * time;
orientation += rotation * time;
//속도 갱신
velocity += steering.linear * time;
rotation += steering.angular * time;
}생략하면 위처럼 간결해진다.
근데 이거 괜찮을까? 그래서 시뮬레이션 돌려봤다.
둘 다 꽤 비슷하다. 오차는 2%정도 생겼다.
방향
많은 게임이 캐릭터의 방향을 이동하는 방향으로 설정한다.
아래와 같이 삼각함수로 표현할 수 있다.
public static float OrientationFromVelocity(Vector3 velocity)
{
return Mathf.Atan2(velocity.x, velocity.z) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
}
방향을 벡터로 표현할때도 삼각함수를 이용하면 쉽다.
public static Vector3 Orientation2Vector(float orientation)
{
return new Vector3(Mathf.Sin(orientation * Mathf.Deg2Rad),
0f,
Mathf.Cos(orientation * Mathf.Deg2Rad));
}
kinematic movement 알고리즘 (가속도 없음)
반환값
kinematic 알고리즘은 속도만 사용하고 가속도는 사용하지 않는다. Kinematic 알고리즘은 다음 값들을 반환한다.
public struct KinematicSteeringOutput
{
public Vector3 velocity;
public float rotation;
}
사실 속도를 반환한다고 가속도를 못 쓰는건 아닌데,
public override KinematicSteeringOutput GetSteer(Kinematic character, float deltaTime)
{
var result = new KinematicSteeringOutput();
result.velocity = character.velocity + _currentSteering.linear * deltaTime;
result.rotation = character.rotation + _currentSteering.angular * deltaTime;
return result;
}이런식으로 속도를 반환해주고

이 식을 이용하면 되기 때문
private void UpdateKinematic(KinematicSteeringOutput steering, float deltaTime)
{
var oldVelocity = _kinematic.velocity;
var oldRotation = _kinematic.rotation;
_kinematic.velocity = steering.velocity;
_kinematic.rotation = steering.rotation;
var avgVelocity = (oldVelocity + _kinematic.velocity) * 0.5f;
var avgRotation = (oldRotation + _kinematic.rotation) * 0.5f;
_kinematic.position += avgVelocity * deltaTime;
_kinematic.orientation += avgRotation * deltaTime;
}
찾기 (SEEK & ARRIVAL)
특정 타겟으로 이동하는 알고리즘은 상대방으로 향하는 벡터에 속도를 곱해서 구현할 수 있다.
public class ASObjectMovementFunc_Seek : ASObjectMovementFunc
{
private readonly ASObject _target;
private float _maxSpeed;
public override KinematicSteeringOutput GetSteer(Kinematic character, float deltaTime)
{
var result = new KinematicSteeringOutput();
var distVector = _target.Position - character.position;
result.velocity = distVector.normalized * _maxSpeed;
result.isfacingMoveDir = true;
return result;
}
}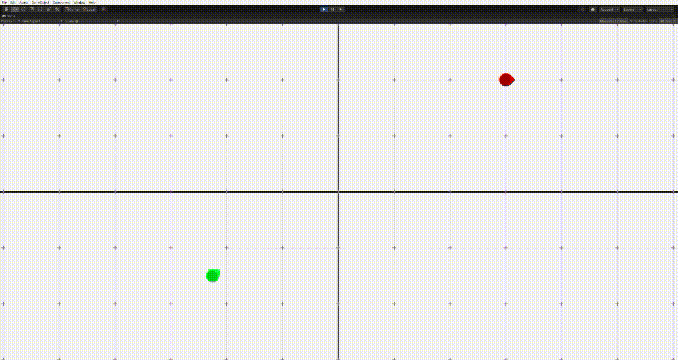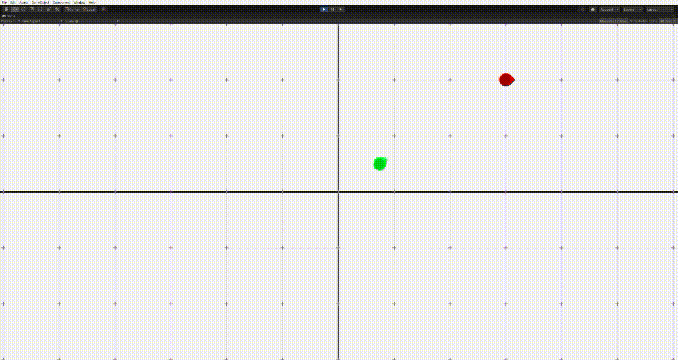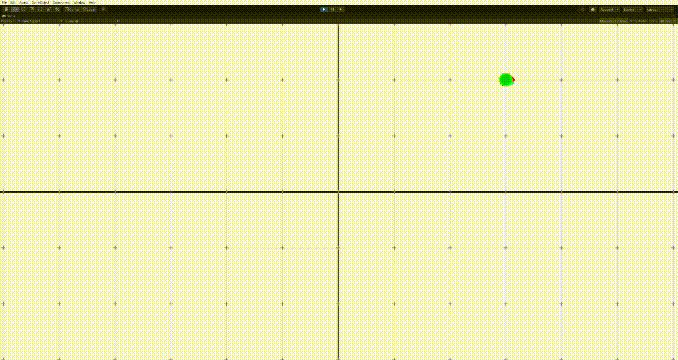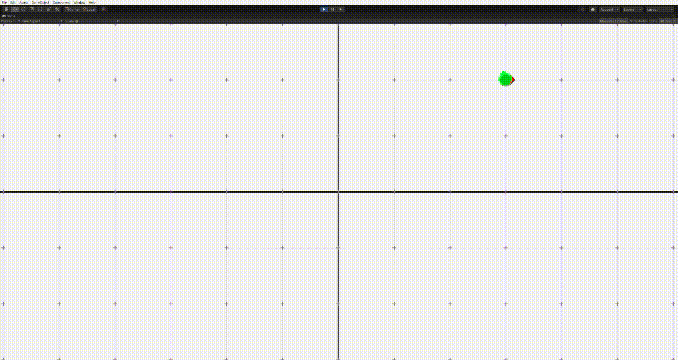
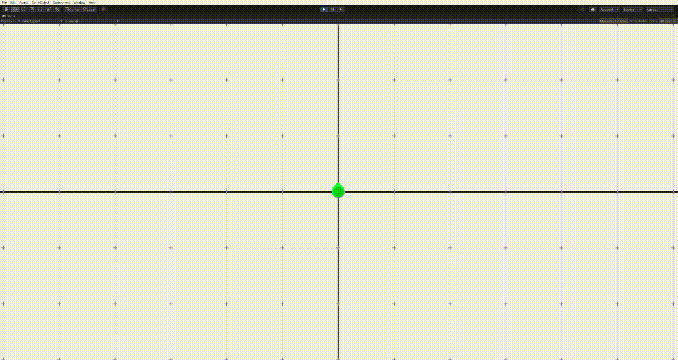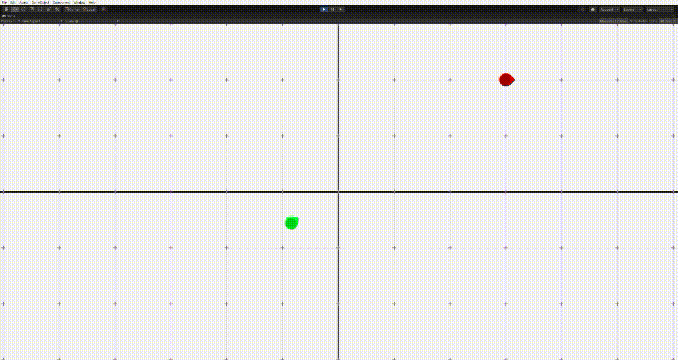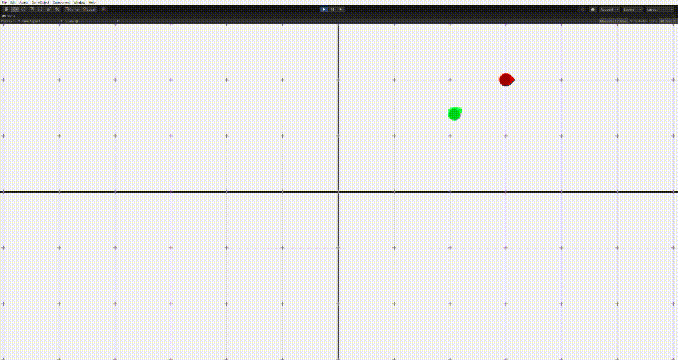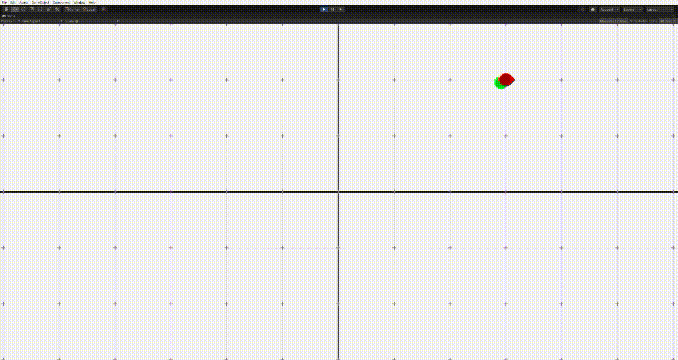
그러나 이 경우 문제가 생기는데, 상대방의 위치에 근접하면 멈추기가 어렵다는 점이다. 그러면 위의 움짤의 마지막같은 문제가 생긴다.
그렇다면 어떻게 타겟에 도달할때 잘 멈출 수 있을까? 두 가지 방법이 있다.
- 일정 반경 안에 들어가면 멈추기
- 가까이 가면 속도를 줄이기
그리고 이 둘을 조합하면 적절하게 멈추는 알고리즘을 구현할 수 있다.
public class ASObjectMovementFunc_Arrive : ASObjectMovementFunc
{
private readonly ASObject _target;
private float _maxSpeed;
private const float TimeToTarget = 0.25f;
private const float SatisfactionRadiusSqr = 100f;
public override KinematicSteeringOutput GetSteer(Kinematic character, float deltaTime)
{
var distVector = _target.Position - character.position;
//근처에 가면 멈춘다
if (distVector.sqrMagnitude < SatisfactionRadiusSqr)
return default(KinematicSteeringOutput);
var result = new KinematicSteeringOutput();
result.velocity = distVector / TimeToTarget;
//너무 빠르면 최대속도로 설정한다.
if (result.velocity.sqrMagnitude > _maxSpeed * _maxSpeed)
result.velocity = result.velocity.normalized * _maxSpeed;
return result;
}
}
배회하기
배회하는 이동의 경우 캐릭터가 바라보는 방향을 무작위로 설정해주고 해당 방향으로 이동하게 만들면 된다.
public class ASObjectMovementFunc_Wander : ASObjectMovementFunc
{
private readonly float _maxSpeed = 50.0f;
private readonly float _maxRotation = 180f;
public override KinematicSteeringOutput GetSteer(Kinematic character, float deltaTime)
{
var result = new KinematicSteeringOutput();
result.velocity = _maxSpeed * character.OrientationVector;
result.rotation = ASFunc.PseudoBinomialRandom() * _maxRotation;
return result;
}
}
여기서 PseudoBinomialRandom은 이항분포(정규분포) 의 그래프와 유사한 랜덤값을 받는다. (삼각형 모양의 그래프)
이건 아래와 같이 굉장히 빠르고 간편하게 구할 수 있다.
public static float PseudoBinomialRandom(float min = -1f, float max = 1f)
{
return Random.Range(min, max) - Random.Range(min, max);
}
참고 : Ian Millington, AI for GAMES 3rd edition, CRC press, [41~56p]
'Game AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Game AI - Steering Behaviors (3) (1) | 2021.10.03 |
|---|---|
| Game AI - Steering Behaviors (2) (1) | 2021.08.07 |
| Game AI - Steering Behaviors (1) (4) | 2021.06.19 |
| 게임 AI의 구현 (2) | 2021.05.31 |
| 게임 AI의 모델 (0) | 2021.05.24 |